924
Lectures Watched
Since January 1, 2014
Since January 1, 2014
- A History of the World since 1300 (68)
- History of Rock, 1970-Present (50)
- A Brief History of Humankind (48)
- Chinese Thought: Ancient Wisdom Meets Modern Science (35)
- The Modern World: Global History since 1760 (35)
- The Bible's Prehistory, Purpose, and Political Future (28)
- Introduction aux éthiques philosophiques (27)
- Jesus in Scripture and Tradition (25)
- Roman Architecture (25)
- Sexing the Canvas: Art and Gender (23)
- Descubriendo la pintura europea de 1400 a 1800 (22)
- Introduction aux droits de l'homme (19)
- Buddhism and Modern Psychology (18)
- Calvin: Histoire et réception d'une Réforme (17)
- The Ancient Greeks (16)
- À la découverte du théâtre classique français (15)
- The French Revolution (15)
- Letters of the Apostle Paul (14)
- Key Constitutional Concepts and Supreme Court Cases (14)
- Christianisme et philosophie dans l'Antiquité (14)
- Egiptología (12)
- Western Music History through Performance (10)
- The Rise of Superheroes and Their Impact On Pop Culture (9)
- The Great War and Modern Philosophy (9)
- Alexander the Great (9)
- Greek and Roman Mythology (9)
- Human Evolution: Past and Future (9)
- Phenomenology and the Conscious Mind (9)
- Masterpieces of World Literature (8)
- Villes africaines: la planification urbaine (8)
- Greeks at War: Homer at Troy (7)
- Pensamiento Científico (7)
- MongoDB for Node.js Developers (7)
- Fundamentos de la escritura en español (7)
- Introduction to Psychology (7)
- Programming Mobile Applications for Android (7)
- The Rooseveltian Century (6)
- Karl der Große - Pater Europae (6)
- Fake News, Facts, and Alternative Facts (6)
- Reason and Persuasion Through Plato's Dialogues (6)
- The Emergence of the Modern Middle East (6)
- A Beginner's Guide to Irrational Behavior (6)
- Lingua e cultura italiana: avanzata (6)
- L'avenir de la décision : connaître et agir en complexité (5)
- Understanding Einstein: The Special Theory of Relativity (5)
- Dinosaur Paleobiology (5)
- Exploring Beethoven's Piano Sonatas (5)
- War for the Greater Middle East (4)
- Emergence of Life (4)
- Introduction to Public Speaking (4)
- The Kennedy Half Century (4)
- Problèmes métaphysiques à l'épreuve de la politique, 1943-1968 (4)
- Designing Cities (4)
- Western Civilization: Ancient and Medieval Europe (3)
- Paleontology: Early Vertebrate Evolution (3)
- Orientierung Geschichte (3)
- Moons of Our Solar System (3)
- Introduction à la philosophie de Friedrich Nietzsche (3)
- Devenir entrepreneur du changement (3)
- La Commedia di Dante (3)
- History of Rock and Roll, Part One (3)
- Formation of the Universe, Solar System, Earth and Life (3)
- Initiation à la programmation en Java (3)
- La visione del mondo della Relatività e della Meccanica Quantistica (3)
- The Music of the Beatles (3)
- Analyzing the Universe (3)
- Découvrir l'anthropologie (3)
- Postwar Abstract Painting (3)
- The Science of Religion (2)
- La Philanthropie : Comprendre et Agir (2)
- Highlights of Modern Astronomy (2)
- Materials Science: 10 Things Every Engineer Should Know (2)
- The Changing Landscape of Ancient Rome (2)
- Lingua e letteratura in italiano (2)
- Gestion des aires protégées en Afrique (2)
- Géopolitique de l'Europe (2)
- Introduction à la programmation en C++ (2)
- Découvrir la science politique (2)
- Our Earth: Its Climate, History, and Processes (2)
- The European Discovery of China (2)
- Understanding Russians: Contexts of Intercultural Communication (2)
- Philosophy and the Sciences (2)
- Søren Kierkegaard: Subjectivity, Irony and the Crisis of Modernity (2)
- The Fall and Rise of Jerusalem (2)
- The Science of Gastronomy (2)
- Galaxies and Cosmology (2)
- Introduction to Classical Music (2)
- Art History for Artists, Animators and Gamers (2)
- L'art des structures 1 : Câbles et arcs (2)
- Russian History: from Lenin to Putin (2)
- The World of Wine (1)
- Wine Tasting: Sensory Techniques for Wine Analysis (1)
- William Wordsworth: Poetry, People and Place (1)
- The Talmud: A Methodological Introduction (1)
- Switzerland in Europe (1)
- The World of the String Quartet (1)
- Igor Stravinsky’s The Rite of Spring (1)
- El Mediterráneo del Renacimiento a la Ilustración (1)
- Science of Exercise (1)
- Социокультурные аспекты социальной робототехники (1)
- Russian History: from Lenin to Putin (1)
- The Rise of China (1)
- The Renaissance and Baroque City (1)
- Visualizing Postwar Tokyo (1)
- In the Night Sky: Orion (1)
- Oriental Beliefs: Between Reason and Traditions (1)
- The Biology of Music (1)
- Mountains 101 (1)
- Moral Foundations of Politics (1)
- Mobilité et urbanisme (1)
- Introduction to Mathematical Thinking (1)
- Making Sense of News (1)
- Magic in the Middle Ages (1)
- Introduction to Italian Opera (1)
- Intellectual Humility (1)
- The Computing Technology Inside Your Smartphone (1)
- Human Origins (1)
- Miracles of Human Language (1)
- From Goddard to Apollo: The History of Rockets (1)
- Hans Christian Andersen’s Fairy Tales (1)
- Handel’s Messiah and Baroque Oratorio (1)
- Theater and Globalization (1)
- Gestion et Politique de l'eau (1)
- Une introduction à la géographicité (1)
- Frontières en tous genres (1)
- Créer et développer une startup technologique (1)
- Découvrir le marketing (1)
- Escribir para Convencer (1)
- Anthropology of Current World Issues (1)
- Poetry in America: Whitman (1)
- Introducción a la genética y la evolución (1)
- Shakespeare: On the Page and in Performance (1)
- The Civil War and Reconstruction (1)
- Dinosaur Ecosystems (1)
- Développement durable (1)
- Vital Signs: Understanding What the Body Is Telling Us (1)
- Imagining Other Earths (1)
- Learning How to Learn (1)
- Miracles of Human Language: An Introduction to Linguistics (1)
- Web Intelligence and Big Data (1)
- Andy Warhol (1)
- Understanding the Brain: The Neurobiology of Everyday Life (1)
- Practicing Tolerance in a Religious Society (1)
- Subsistence Marketplaces (1)
- Physique générale - mécanique (1)
- Exercise Physiology: Understanding the Athlete Within (1)
- Introduction to Mathematical Philosophy (1)
- What Managers Can Learn from Great Philosophers (1)
- A la recherche du Grand Paris (1)
- The New Nordic Diet (1)
- A New History for a New China, 1700-2000 (1)
- The Magna Carta and its Legacy (1)
- The Age of Jefferson (1)
- History and Future of Higher Education (1)
- Éléments de Géomatique (1)
- 21st Century American Foreign Policy (1)
- The Law of the European Union (1)
- Design: Creation of Artifacts in Society (1)
- Introduction to Data Science (1)
- Configuring the World (1)
- From the Big Bang to Dark Energy (1)
- Animal Behaviour (1)
- Programming Mobile Services for Android Handheld Systems (1)
- The American South: Its Stories, Music, and Art (1)
- Care of Elders with Alzheimer's Disease (1)
- Contagious: How Things Catch On (1)
- Constitutional Law - The Structure of Government (1)
- Narratives of Nonviolence in the American Civil Rights Movement (1)
- Christianity: From Persecuted Faith to Global Religion (200-1650) (1)
- Age of Cathedrals (1)
- Controversies of British Imperialism (1)
- Big History: From the Big Bang until Today (1)
- Bemerkenswerte Menschen (1)
- The Art of Poetry (1)
- Superpowers of the Ancient World: the Near East (1)
- America Through Foreign Eyes (1)
- Advertising and Society (1)
Hundreds of free, self-paced university courses available:
my recommendations here
my recommendations here
Peruse my collection of 275
influential people of the past.
influential people of the past.
View My Class Notes via:
Receive My Class Notes via E-Mail:
Contact Me via E-Mail:
edward [at] tanguay.info
Notes on video lecture:
Darwin's Effect on 19th Century Ideas
Notes taken by Edward Tanguay on October 27, 2015 (go to class or lectures)
Choose from these words to fill the blanks below:
natural, artifacts, revolutionary, creatures, Edinburgh, skulls, Galapagos, advisers, different, Beagle, lifetime, global, abolitionist, debased, 1839, shocked, Descent, propensities, adaptation, earth, racial, diversification, Indians, French
•
Charles Darwin
•
developed an early fascination with history
•
educated at and Cambridge
•
encouraged him to explore his world
•
a world that was becoming both interconnected and interdependent
•
an example in which the worlds horizons were opening up
•
technological revolutions
•
Revolution
•
advent of free trade
•
embarked on a five year journey
•
H.M.S.
•
South America
•
Islands
•
Australia
•
gathered evidence of
•
fossils
•
marine invertebrate
•
fascinated by he gathered from various places in the world
•
a good observer of animal behavior
•
last book was a book about worms
•
The Voyage of the Beagle
•
on trip, he took notes and he doodled
•
1850 On the Origin of Species
•
note the singular origin to the plural species
•
he wanted to help explain in nature
•
variation and take place over time
•
concluded that insects became more speciated over time
•
they were not born different, they evolved to become different
•
1871 The of Man and Selection in Relation to Sex
•
his major work
•
based on his of observation of
•
orchids
•
moths
•
animals from around the world
•
argued for a concept of human evolution and sexual selection
•
all humans are one species
•
all species share some fundamental
•
from common descent we get diversity
•
humans among other species belong to a single animal kingdom
•
"Man with all his noble qualities, with sympathy which feels for the most , with benevolence which extends not only to other men but to the humblest living creature, with his god-like intellect which has penetrated into the movements and constitution of the solar system, with all these exalted powers, man still bears in his bodily frame the indelible stamp of his lowly origin."
•
powerful and words
•
and you can imagine the brouhaha that would be produced by words such as these
•
this was a blow to theories about
•
living beings
•
humanity
•
history
•
until Darwin came along, the prevailing dogma was that humans were fundamentally
•
different species obeyed different laws
•
people came from entirely different origins
•
this idea of a fundamental species differentiation among humans was a theory called pluralism
•
used phrenology to examine to determine which race people belonged to
•
put negros at the bottom of the ladder of superiority and inferiority
•
people had to be kept in their places since they were meant to be separate
•
argument for slavery
•
physical characteristics of people showed that we belonged to different races which should stay separate
•
along comes Charles Darwin
•
argued that the laws of natural selection applied to all
•
arguing for a different model
•
in his tree of life, humans all branch from a shared trunk
•
Africans, , Europeans
•
it's often forgotten that he was a lifelong and a profound humanitarian and his science buttressed his moral code
•
he work in his journal The Voyage of Chronicle of the Beagle that he was at the sight of slavery in Brazil and in South Africa
Ideas and Concepts:
How 19th century arguments for slavery were undercut by Darwin's theory of natural selection, via this morning's History Since 1300 class: "The prevailing social dogma of pre-Darwin Europe was that human races were fundamentally different, that each race had fundamentally different characteristics, came from different origins, obeyed different laws, and therefore each had a different place in the world. Pseudoscience such as phrenology was used to examine the skulls of various races to show that some races were more adept at being masters and other races more adept at being slaves, which naturally put negroes at the bottom of the ladder of superiority and inferiority, which was used an argument to justify the institution of slavery in places such as the Southern United States, Brazil, and South Africa. Then along came Charles Darwin who argued that the laws of natural selection applied to all creatures and that humans all branch from a shared trunk, showing that Africans, Indians, and Europeans did not come from different origins at all, but from the same origin, a theory which undermined the argument for slavery and was anathema to those who were benefiting economically and socially from the institution of slavery."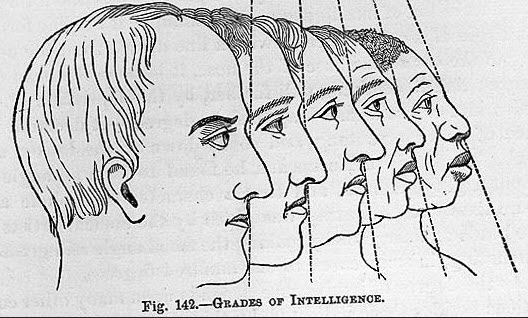
Pseudoscience of the day, via this morning's History Since 1300 class: "phrenology, n. from [φρήν] (mind) and [λόγος] (knowledge), a study primarily focused on measurements of the human skull, based on the concept that the brain is the organ of the mind, and that certain brain areas have localized, specific functions or modules. Although both of those ideas have a basis in reality, phrenology extrapolated beyond empirical knowledge in a way that departed from science. Developed by German physician Franz Joseph Gall in 1796, the discipline was very popular in the 19th century, especially from about 1810 until 1840. Although now regarded as an obsolete amalgamation of primitive neuroanatomy with moral philosophy, phrenological thinking was influential in 19th-century psychiatry. Gall's assumption that character, thoughts, and emotions are located in specific parts of the brain is considered an important historical advance toward neuropsychology."